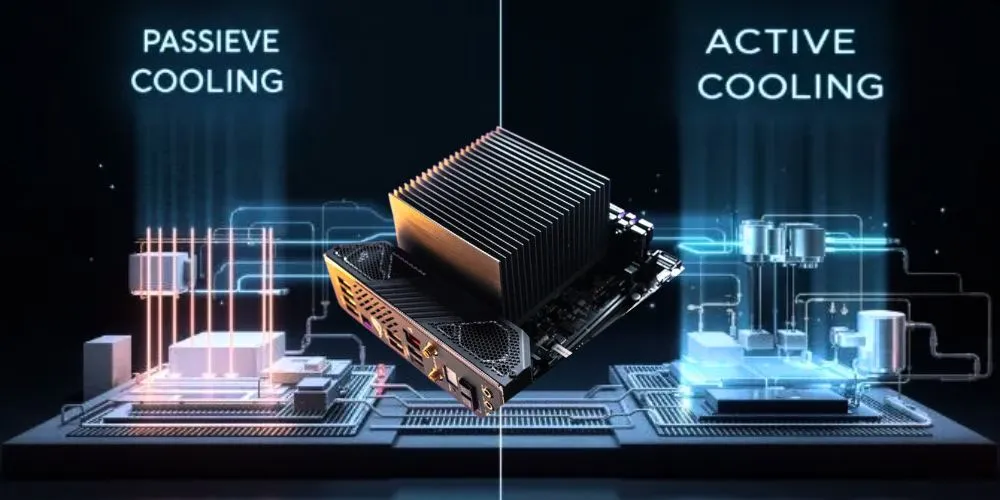
For years, active cooling solutions like fans and liquid coolers have dominated the PC industry, ensuring that processors, graphics cards, and other components stay within safe temperatures. However, passive cooling systems quietly become modern hardware, offering silent, efficient, and maintenance-free cooling. While often overlooked, passive cooling is becoming a viable alternative for many users who prioritize noise reduction, reliability, and energy efficiency.
How Passive Cooling Works
Unlike traditional cooling methods that rely on fans or pumps to dissipate heat, passive cooling systems use heatsinks, vapor chambers, and advanced materials to manage temperatures without moving parts. By leveraging heat spreaders, natural convection, and thermal conductivity, passive coolers efficiently transfer heat away from components, eliminating the need for power-hungry and noisy cooling solutions.
The Advantages of Silent Operation
One of the most significant selling points of passive cooling is silent operation. Fans generate noise, especially under heavy workloads, which can be distracting in workspaces, home offices, and media setups. Passive cooling eliminates this issue, providing a genuinely silent computing experience. This makes it ideal for fanless laptops, industrial PCs, home theater systems (HTPCs), and even gaming consoles that benefit from a noise-free environment.
Increased Reliability and Longevity
Since passive cooling systems lack moving parts, they are less prone to failure than fan-based solutions. Fans accumulate dust, wear out over time, and eventually fail, leading to overheating and performance issues. On the other hand, passive coolers have a longer lifespan and require little to no maintenance. This makes them an attractive choice for mission-critical systems, embedded devices, and long-term industrial applications where reliability is crucial.
The Future of Passive Cooling in High-Performance Systems
While passive cooling has traditionally been limited to low-power devices, advancements in thermal materials and cooling technology are making it possible to integrate passive cooling into higher-performance PCs and gaming rigs. Companies are experimenting with graphene-based heatsinks, phase-change cooling, and sizeable surface-area cooling solutions that could someday make fanless high-performance systems a reality. As power efficiency improves, passive cooling may become a mainstream alternative to traditional cooling methods.
Conclusion
The rise of passive cooling systems represents a quiet revolution in PC hardware. Offering silent operation, increased reliability, and reduced maintenance, passive cooling is becoming an attractive choice for users seeking a more efficient and noise-free experience. While it may not replace active cooling entirely, the future of fanless computing is looking brighter than ever, and it’s only a matter of time before it becomes a standard feature in more devices.