High-performance PCs are designed for demanding tasks like gaming, content creation, and professional workloads, often requiring powerful hardware that generates significant heat and noise. Excessive noise from fans, power supplies, and other components can distract, reducing overall user comfort and focus. Fortunately, modern advancements in cooling solutions and noise-reducing hardware provide effective ways to achieve a quieter PC without sacrificing performance. Understanding the sources of noise and implementing the right strategies can help build a powerful yet silent computing environment.
Understanding Noise in High-Performance PCs
PC noise primarily originates from mechanical components such as cooling fans, hard drives, and power supplies. As high-performance systems generate more heat due to powerful processors and graphics cards, cooling mechanisms must work harder, often increasing noise levels. The noise intensity can be influenced by airflow obstruction, component vibration, and poor case design. Identifying these noise sources is the first step in effectively reducing them.
Cooling Solutions for Noise Reduction
Efficient cooling is essential in minimizing noise, as excessive heat forces fans to spin at higher speeds, producing more sound. Implementing advanced cooling solutions can significantly lower noise levels while maintaining optimal thermal performance.
High-Quality Case Fans
Replacing stock fans with high-quality, low-noise alternatives can dramatically reduce PC noise. Premium fans feature fluid dynamic or magnetic levitation bearings, which offer quieter operation and longer lifespans. Additionally, larger fans can move the same amount of air at lower speeds, reducing overall noise levels. Optimizing fan placement and airflow direction also improves cooling efficiency, allowing for lower fan speeds and quieter performance.
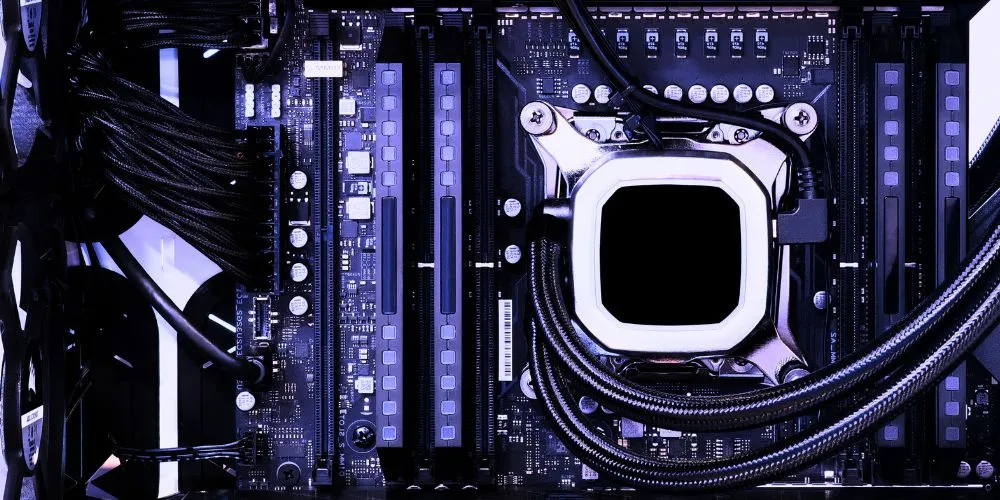
Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling provides an effective way to manage high temperatures without relying solely on traditional air cooling. Closed-loop all-in-one (AIO) coolers and custom liquid cooling loops use liquid coolant to dissipate heat more efficiently than standard air coolers. Because liquid cooling requires fewer high-speed fans, it often results in a quieter system, especially under heavy loads. Radiator placement and pump noise should be considered to maximize efficiency and minimize vibrations.
Fan Speed Control and Custom Profiles
Adjusting fan speed profiles through BIOS settings or software utilities can help balance cooling performance and noise levels. Many motherboards and fan controllers allow users to set custom fan curves, ensuring that fans only ramp up when necessary. Running fans at lower speeds during idle or low-load conditions reduces unnecessary noise while maintaining adequate cooling.
Hardware Choices for Quieter Performance
Selecting the right hardware components plays a crucial role in noise reduction. Modern advancements in PC hardware allow users to build high-performance systems with minimal acoustic output.
Silent Power Supplies
Power supplies (PSUs) with high-efficiency ratings, such as 80 Plus Gold or Platinum, generate less heat, reducing the need for aggressive cooling. Many high-quality PSUs feature semi-passive or fully passive cooling modes, where the fan remains off under low loads, producing near-silent operation. Choosing a PSU with sufficient wattage headroom prevents excessive heat buildup and unnecessary fan noise.
Low-Noise Graphics Cards
Graphics cards are among the loudest components in high-performance PCs, especially under heavy workloads. Many modern GPUs feature advanced cooling solutions with larger heatsinks and quiet fans that remain idle during low-power tasks. Some premium models use hybrid cooling, combining passive and liquid cooling to achieve lower temperatures with minimal noise. Undervolting the GPU can also help reduce heat output, allowing fans to run at lower speeds.
SSDs Instead of HDDs
Traditional mechanical hard drives (HDDs) produce noise from spinning platters and moving read/write heads. Replacing HDDs with solid-state drives (SSDs) eliminates this noise source while providing faster data access and improved reliability. NVMe SSDs connect directly to the motherboard, further reducing vibrations and case clutter and contributing to a quieter system.
Case Design and Noise Dampening
The design of the PC case plays a significant role in noise reduction. Well-engineered cases include features that minimize sound while maintaining efficient cooling.
Sound-Dampening Materials
Some cases come equipped with noise-dampening materials such as foam padding, rubber grommets, and insulated panels to absorb vibrations and reduce sound leakage. These materials help lower fan noise and suppress the hum of internal components, creating a quieter operating environment.
Optimized Airflow Design
A well-ventilated case allows for better airflow, reducing the need for high-speed fans. Cases with spacious layouts, cable management features, and proper intake and exhaust configurations promote efficient cooling while keeping noise levels low. Mesh front panels and additional fan mounting options allow for improved ventilation without increasing fan speeds.
Vibration Reduction Features
Vibrations from mechanical components can amplify noise, especially in poorly designed cases. Features such as rubberized hard drive mounts, PSU dampening brackets, and anti-vibration fan mounts help isolate and minimize vibrations, reducing overall system noise. Ensuring all components are securely fastened can further prevent unnecessary rattling and resonance.
Software-Based Noise Reduction Techniques
Software utilities can help manage noise levels by controlling fan speeds, optimizing power consumption, and adjusting performance settings.
Smart Fan Control Software
Many motherboard manufacturers provide fan control software that allows users to customize fan speed profiles based on system temperature. Applications such as MSI Afterburner, Corsair iCUE, and ASUS Fan Xpert enable fine-tuning fan behavior, ensuring quiet operation without compromising cooling efficiency.
Undervolting and Power Management
Undervolting the CPU and GPU reduces power consumption and heat output, allowing cooling fans to operate at lower speeds. This technique can be achieved through BIOS settings or software utilities like Intel XTU and AMD Ryzen Master. Additionally, enabling power-saving modes for the CPU and GPU can further reduce heat generation and fan noise during less demanding tasks.
Noise-Canceling Technologies
Some modern headsets and speakers feature active noise-canceling technology, which can help mitigate background noise from PC fans. While this does not directly reduce PC noise, it enhances the user experience by minimizing distractions caused by system sounds.
Future Trends in Silent PC Design
Manufacturers are developing innovative solutions to create quieter, high-performance systems as PC hardware evolves.
Fanless Cooling Solutions
Advancements in passive cooling technology are making fanless PC designs more viable. Large heatsinks, heat pipes, and vapor chambers are integrated into CPUs and GPUs to dissipate heat without requiring active cooling. This trend is particularly beneficial for compact and noise-sensitive environments.
AI-Driven Cooling Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being integrated into cooling solutions to optimize fan speeds and power management dynamically. AI-driven fan controllers analyze real-time temperature data and workload patterns to adjust cooling performance automatically, reducing noise without compromising thermal efficiency.
Eco-Friendly and Noise-Reducing Materials
Manufacturers are incorporating eco-friendly materials and advanced composites into case design to enhance noise reduction while maintaining sustainability. Recycled acoustic insulation and innovative airflow-enhancing materials are being explored to create quieter and more environmentally friendly PC cases.
Conclusion
Reducing noise in high-performance PCs requires a combination of hardware upgrades, optimized cooling solutions, and effective noise-dampening techniques. By selecting high-quality components, implementing smart cooling strategies, and utilizing software-based controls, users can achieve a powerful yet quiet computing experience. As technology advances, silent PC designs are becoming more accessible, allowing enthusiasts and professionals to enjoy high-performance computing without the distraction of excessive noise.